The research project
Rising ambient temperatures due to global climate change exacerbate building overheating, heighten energy demand and indoor environmental quality concerns, impact human health, and worsen urban heat islands (UHI) in densely populated areas. Despite recognition of UHI’s significant influence on building energy efficiency, challenges persist in accurately quantifying its effects due to limited microscale climatic data and modeling complexities. While Urban Building Energy Modeling (UBEM) offers potential, it struggles to address UHI adequately due to data scarcity. The CRiStAll project aims to bridge these gaps by creating high-resolution climatic datasets and assessing UHI effects on Italian building archetypes across various urban contexts and climate zones. By simulating future climate scenarios and urban configurations, the project seeks to enhance climate resilience through surface treatments and building technologies, generating key performance indicators for energy efficiency and thermal comfort. These findings aim to inform policymakers on energy strategies, offering insights into UHI intensity across urban areas for informed decision-making.
The research lines
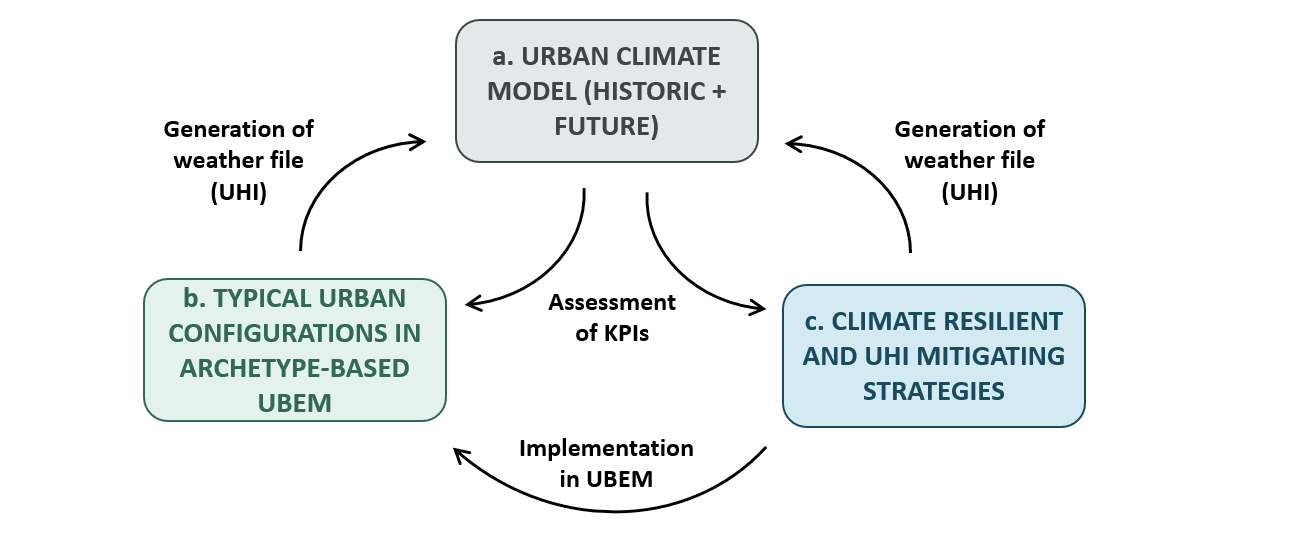
The questions that CRiStAll will answer
• How to develop urban climate models fit to assess the building energy performance in the future, taking into account the “dynamism” of the UHI with climate changes (future weather data)?
• Is it possible to combine the urban microclimate variables with the building archetypes, as to generate typical urban configurations easily exploitable in UBEMs, thus increasing the spatial coverage of UHI analyses?
• What technical solutions can be adopted to mitigate the UHI and the climate change effects, thus enriching the archetype approach with resilient technologies?

